-Video-_-Facebook-—-Mozilla-Firefox.png)
Mastering Memory: How to Overcome the Forgetting Curve and Boost Information Retention
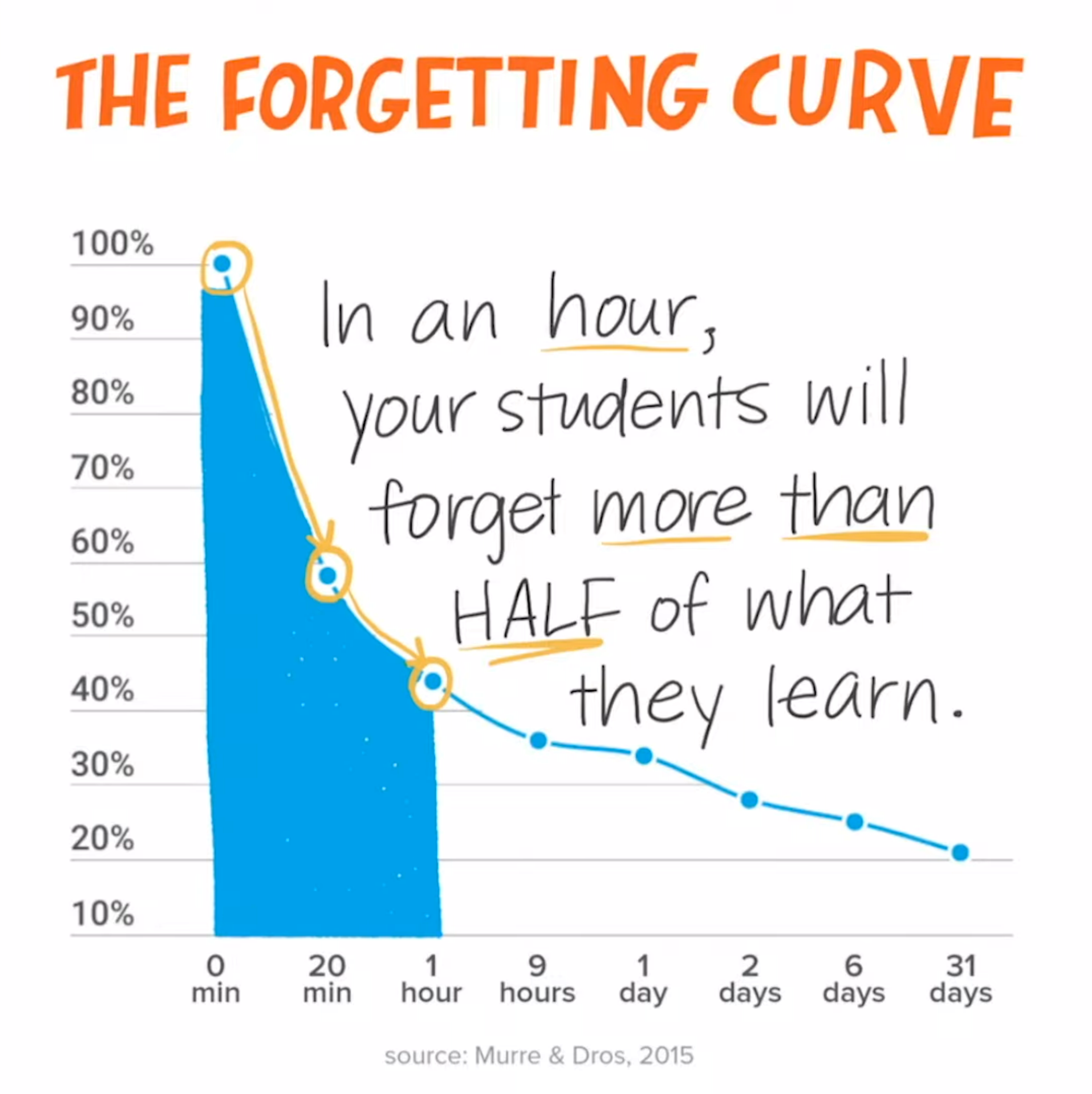
In the quest for knowledge, one of the most frustrating experiences is the sensation of forgetting information we've worked so hard to learn. This phenomenon is well-documented in psychology and is known as the Forgetting Curve. First described by Hermann Ebbinghaus in the late 19th century, and later expanded upon by researchers like Murre and Dross in their 2015 study, the Forgetting Curve illustrates how quickly we lose information over time if we don't actively review and reinforce it.
Understanding the Forgetting Curve is the first step in combating memory loss, but it’s the strategies you employ to retain information that make all the difference. Let’s delve into how the Forgetting Curve works and explore effective techniques to improve your information retention.
The Forgetting Curve describes the exponential decline of memory retention over time. Ebbinghaus’s original research found that we forget a significant portion of newly learned information within just a few hours, with the rate of forgetting leveling off over time. Murre and Dross’s 2015 review built upon this by analyzing more recent studies, reinforcing that without reinforcement, we typically lose about 50% of new information within an hour, and up to 70% within a day.
1. Spaced Repetition: One of the most powerful tools for improving memory retention is spaced repetition. This technique involves reviewing information at increasing intervals. For example, if you learn a new concept today, you might review it again tomorrow, then a week later, and then a month later. This method leverages the brain’s natural tendency to better remember information that is repeatedly encountered over time. Tools like Anki or Quizlet can help automate this process with flashcards.
2. Active Recall: Active recall is a technique that involves testing yourself on the material you want to remember rather than passively rereading it. For instance, after studying a chapter of a textbook, close it and try to write down or recite the main points from memory. This process strengthens neural connections associated with the learned material and enhances long-term retention.
3. Interleaved Practice: Instead of studying one topic in isolation, mix different subjects or types of problems in a single study session. This technique, known as interleaved practice, helps improve the brain’s ability to differentiate between concepts and apply knowledge more flexibly. For example, if you’re studying math, work on a variety of problems involving different techniques rather than focusing on just one type.
4. Elaborative Interrogation: This technique involves asking yourself why the information you are learning is true and how it relates to what you already know. By making connections between new information and existing knowledge, you create a richer and more integrated memory network. For instance, if you’re learning about a historical event, ask yourself how it influenced subsequent events or relate it to similar events in other countries.
5. Mnemonic Devices: Mnemonics are memory aids that help you recall information more easily. Techniques like acronyms, visualization, and rhymes can make abstract or complex information more tangible. For example, to remember the order of the planets in our solar system, you might use the mnemonic “My Very Eager Mother Just Served Us Nachos” (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune).
6. Teach What You’ve Learned: Teaching someone else what you’ve just learned is a powerful way to reinforce your own understanding. Explaining concepts to others requires you to organize your thoughts and clarify your understanding, which in turn helps solidify your own knowledge. This method, often referred to as the “Feynman Technique,” encourages deeper learning and retention.
7. Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Your physical health significantly impacts cognitive function and memory. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management all contribute to better memory retention. Ensuring that you maintain a healthy lifestyle can provide a solid foundation for effective learning and memory.
To effectively counteract the Forgetting Curve, it’s essential to employ a combination of these techniques. Spaced repetition and active recall are cornerstones of effective study habits, while strategies like interleaved practice and elaborative interrogation help deepen understanding and application. Mnemonics and teaching reinforce memory through creative and interactive methods, and a healthy lifestyle supports cognitive function.
Incorporating these practices into your learning routine can transform how you retain information and reduce the frustration of forgetting. By actively engaging with material and applying these proven techniques, you’ll be better equipped to master and retain knowledge for the long haul.
At Full Spectrum our learning program consists of a structured weekly session delivery. We found early on that frequent interruptions to sustained lesson delivery or unpredictable teaching schedules resulted in outcomes that were not meeting our expectations. Ensuring retention is maximised by allowing for consistent spaced repetition & delivering content using other memory retention tools has allowed us to achieve amazing results for so many of our students.
Want to keep up to date with all news Full Spectrum? We operate across Australia with large presences in Brisbane, Sydney, Melbourne &
Adelaide as well as many regions like the Sunshine & Gold Coast.
Follow our socials:
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/18361706/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/fullspectrumeducation/
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgnnLc8w9Z_qVAcqmkm_Ryg
Spotify: https://podcasters.spotify.com/pod/show/fullspectrumeducation
X: https://x.com/fseduau